Gross Method of Accounting for Cash Discounts

Suppose Company A sells certain goods at a price of $4,400 with terms of payment of 2/10, n/20. Firstly, the customer must pay within 20 days after the sale or, in other words, they have right to postpone the payment up to the 20th day after sale. Secondly, if the payment is made within 10 days, the customer will also be entitled to a 2% cash discount. Since most customers would rather benefit from the cash discount, such a practice encourages customers to pay early.
Accuracy
In this method, vendor does not make the assumption that the customer will prepay and avail the cash discount. Multiple entries are made at different points of time in the transaction flow to account for sales and cash discount availed by the customer. While gross revenue shows the potential cash inflow from sales, this data point doesn’t account for how much the company will actually keep.
Gross Method vs. Net Method (Seller Transactions)
From 1 January 2024, the components which must be included when calculating ‘normal’ rate of pay are defined in regulations. On the other hand, the gross method may initially inflate both revenues and expenses, leading to a higher reported taxable income until adjustments are made. This can result in temporary discrepancies in tax reporting, which may complicate tax planning and compliance. Businesses using the gross method must be diligent in tracking and reporting discounts separately to ensure that their tax filings accurately reflect their financial activities. This additional layer of complexity can increase the administrative burden and the risk of errors in tax reporting. Businesses often seek efficient ways to manage their financial transactions, and accounting methods play a crucial role in this process.
Accounting For Purchase Discounts: Net Method Vs. Gross Method
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations taxing working and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
In terms of cash flow management, the gross method may not provide the same level of foresight as the net method. Since discounts are not anticipated upfront, businesses may find it harder to predict their actual cash needs and availability. This can be particularly problematic for companies with tight cash flow constraints, as unexpected adjustments can disrupt financial planning and liquidity management. The cash purchase discounts refer to the discount received when a business settles the payment within the credit term. In this term, it means that the business would receive a cash discount of 2% if the business makes payment within the credit term of 30 days.
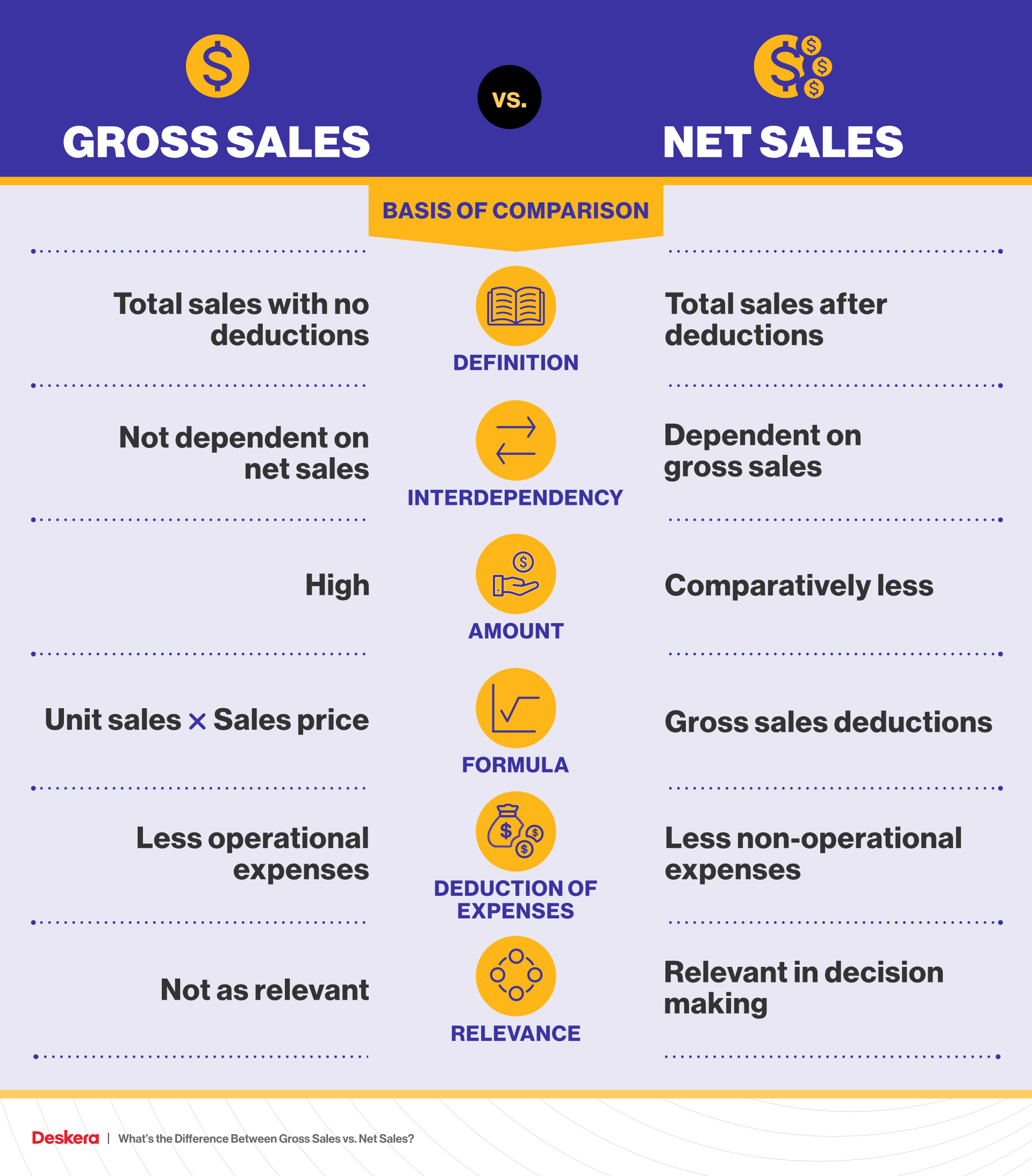
By analyzing historical gross revenue, you can spot patterns that can help predict future sales, such as which quarters typically have higher sales. You can then use this information to set more accurate targets, which makes it easier to plan for growth and more effectively allocate resources. Keep in mind that investors look at both numbers when deciding whether to invest in a company. Gross revenue is used to assess the company’s overall sales strength and growth potential.
- Secondly, if the payment is made within 10 days, the customer will also be entitled to a 2% cash discount.
- Businesses using the gross method must be diligent in tracking and reporting discounts separately to ensure that their tax filings accurately reflect their financial activities.
- Under the gross price method, the purchase discount is only recorded when it is actually taken by making an early payment.
- The net method records transactions after deducting any discounts, returns, or allowances, providing a more conservative view of a company’s financial performance.
- The vendor issues a Credit Memo anyway and we remove the items from inventory and dispose of them.
- The process of adjusting for uncollectible accounts involves estimating the amount of receivables that are unlikely to be collected and recording this estimate as an expense.
If their employer chooses to use rolled-up holiday pay, then the entire amount of their leave for irregular hours and part-year workers will be paid at the ‘normal’ rate of pay. The net method works by recording any purchase discounts obtained from suppliers as an immediate offset to the cost of goods purchased. Accounts receivable will reflect the total amount billed to customers, providing a clear picture of the company’s outstanding invoices. This can be particularly useful for assessing the company’s liquidity and credit management practices.
Businesses must first identify the discount terms, which are often stated as a percentage and a time frame, such as 2/10, n/30. This notation means a 2% discount is available if the invoice is paid within 10 days, with the net amount due in 30 days. By applying the discount percentage to the total invoice amount, companies can determine the net amount to be recorded.
The net method also has implications for financial ratios, which are critical tools for investors and analysts. Ratios such as the current ratio and quick ratio, which measure a company’s liquidity, can be more accurately assessed when liabilities are recorded at their net amounts. This accuracy can lead to more informed decision-making by stakeholders, as the financial statements provide a more realistic view of the company’s short-term financial obligations.
On the other hand, it creates an extra journal entry if they decide to pay their bill early. A key aspect of proper accounting is maintaining record of expenses through Source Documents, paper or evidence of transaction occurrence. See the purpose of source documents through examples of well-kept records in accounting. The credit balance indicates the amount that company or organization owes to its suppliers or vendors. Before we dive into the COGS details for the periodic system, begin to familiarize yourself with this chart. This is a quick way to compare the differences between how the two methods record the details involved with inventory.
By focusing on net figures, it can underrepresent the total volume of transactions, potentially leading to an undervaluation of the company’s market presence and operational capabilities. This can be a disadvantage when seeking to attract new investors or partners who may be interested in the company’s gross performance metrics. Net revenue, on the other hand, gives a realistic view of cash flow because you can see the amount of money that comes in after deductions. Since net revenue represents the amount of cash on hand, you can avoid liquidity issues by planning based on expected income. For example, a retailer sells a large volume of t-shirts, creating a high gross revenue. However, they produced a number of holiday specific t-shirts and ended up heavily discounting these items by mid-December to make sure they sold their inventory.



