How to Make Entries for Accrued Interest in Accounting

They did this because thecost of the premium plus the 5% interest on the face value ismathematically the same as receiving the face value but paying 4%interest. Aswe go through the journal entries, it is important to understandthat we are analyzing the accounting transactions from theperspective of the issuer of the bond. For example, on the issue date of a bond, the borrowerreceives cash while the lender pays cash. When a company issues bonds, it incurs a long-term liability on which periodic interest payments must be made, usually twice a year.
Interest Payment: Issued at a Premium
Interest Expense will be closed automatically at the end of each accounting year and will start the next accounting year with a $0 balance. How you create an accrued interest journal entry depends on whether you’re the borrower or lender. The interest expense of $12,500 incurred during 2020 must be charged to the income statement for the year 2020. The 860,653 value means that this is a premium bond and the premium will be amortized over its life.
What is Accounts Payable? Definition, Recognition, and Measurement, Recording, Example
Credits, in this case, are usually made for interest payable since that account is a liability, and credits increase liabilities. Long-term debts, on the other hand, such as loans for mortgage or promissory notes, are paid off for periods longer than a year. Short-term debts are paid within 6 months to a year and include lines of credit, installment loans, or invoice financing.
Issued When Market Rate Equals Contract Rate
- Our mission is to provide entrepreneurs and small business owners with the knowledge and resources they need.
- Notes payable is a liability that results from purchases of goods and services or loans.
- To accomplish this process, the Discount on Notes Payable account is written off over the life of the note.
- At some point, a company will need to record bondretirement, when the company pays the obligation.
- Welcome to AccountingFounder.com, your go-to source for accounting and financial tips.
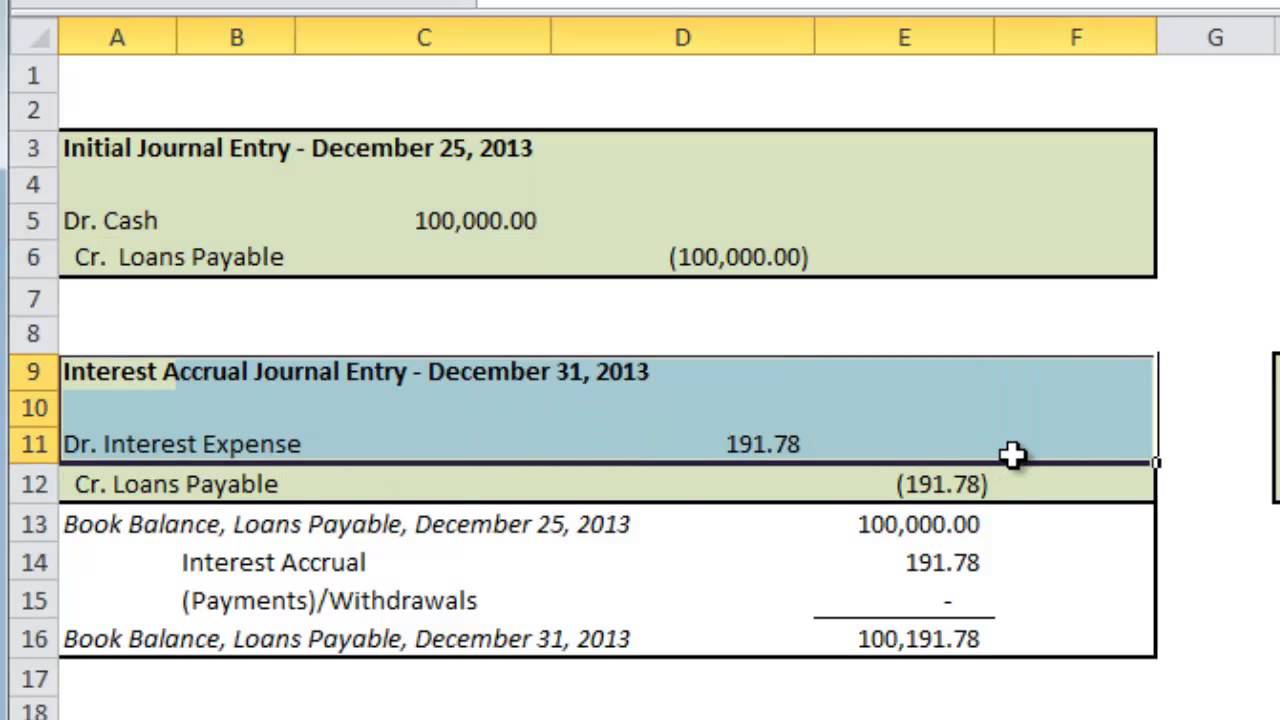
Whether you are the lender or the borrower, you must record accrued interest in your books. The interest expense is the bond payable account multiplied by the interest rate. The payable is a temporary account that will be used because payments are due on January 1 of each year. And finally, there is a decrease in the bond payable account that represents the amortization of the premium.
Usually, any written instrument that includes interest is a form of long-term debt. Computing long-term bond prices involves finding present values using compound interest. Buyers and sellers negotiate a price that yields the going rate of interest what is meant by nonoperating revenues and gains for bonds of a particular risk class. The price investors pay for a given bond issue is equal to the present value of the bonds. As shown above, if the market rate is lower than the contract rate, the bonds will sell for more than their face value.
How to Record Accrued Interest in Your Books
Interest payable amounts are usually current liabilities and may also be referred to as accrued interest. The interest accounts can be seen in multiple scenarios, such as for bond instruments, lease agreements between two parties, or any note payable liabilities. Let’s assume that the company borrowed the $5,000 on December 1 and agrees to make the first interest payment on March 1.
The note in Case 2 is drawn for $5,200, but the interest element is not stated separately. Therefore, in reality, there is an implied interest rate in this transaction because Ng will be paying $18,735 over the next 3 years for what it could have purchased immediately for $15,000. According to Statista theamount of mortgage debt—debt incurred to purchase homes—in theUnited States was $14.9 trillion on 2017.
Until that time, the future obligation might be noted in the notes to the financial statements published in the annual reports. However, the accrued interest expenses may show up in a different Accrued Interest Liability account on the statement of financial position. This is because the maturity of interest payable is generally within twelve months.
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.



